normal end tidal co2 uk
Carbon dioxide during ventilation. If EtCO 2 is 45 to 50mmHg.

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice
Technically this is only when it is measured as a.

. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor. This clears the dead space where no CO2 is produced. The Inspired Level of Carbon dioxide is referred to as P i CO 2 in millimetres of Mercury mmHg.
According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg. End tidal Co2 ranges vary slightly from actual PaCo2 and can be affected by many factors depending on the condition of the patients lungs. This is due to CO2 from the alveoli now reaching the upper airway.
For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5. Capnography is the measurement and numerical display of end-tidal carbon dioxide also known as EtCO 2. End-tidal Carbon dioxide during shock may predict massive transfusion.
Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function. Objectives In the UK 20 of patients with severe traumatic brain injury TBI receive prehospital emergency anaesthesia PHEA.
If patient is immediately aroused and breathing normally monitor every 15 minutes x 1 hour. INTRODUCTION An indication of the adequacy of the intra-vascular volume is of importance in critically ill patients. The end-tidal level of carbon dioxide is generally less but is reflective of carbon dioxide in arterial blood and can serve as an indirect noninvasive method of assessing the adequacy ventilation.
Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. End - tidal CO2 in the diagnosis of fluid responsiveness - a systematic review. In a study of 191 blunt trauma patients only 5 of patients with an end-tidal CO2 determination of 325 kPa survived to discharge.
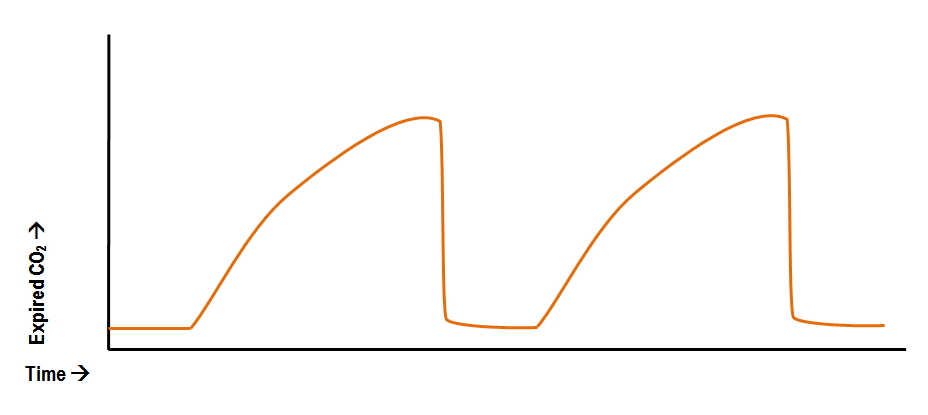
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO 2 in the respiratory gasesIts main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive careIt is usually presented as a graph of expiratory CO 2 measured in millimeters of mercury mmHg plotted against time or less commonly but more usefully. Trauma 2004 showed that end-tidal CO2 may be of value in predicting outcome from major trauma 19. An end-tidal capnography waveform is a simple graphic measurement of how much CO 2 a person is exhaling.
Attempt to stimulate and arouse the patient. There is a green shaded area on each diagram representing normal P E CO 2. End tidal CO 2 EtCO 2.
Capnograms in infants and children can have the following format under normal circumstances due to faster respiratory rates smaller tidal volumes and relatively longer response time of capnographs dispersion of gases in side-stream capnographs. If there is a leak in the system however it will look like the diagram here. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords.
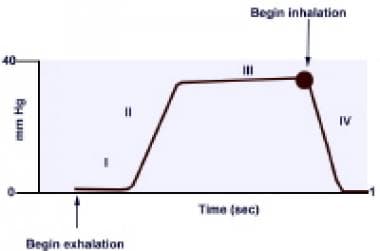
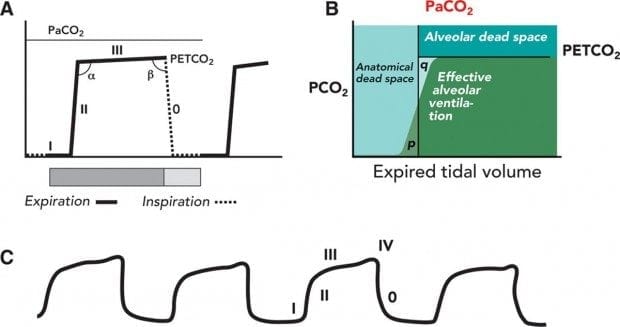
In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. 2 See Figure. The End Tidal Carbon dioxide level is referred to as P E CO 2 in millimetres of Mercury.
The difference between nend-tidal and arterial CO 2 is increased if there is mismatch of ventilation and perfusion within the lung as occurs in lung disease. ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation.
EtCO 2 35-45 mm Hg. In normal lungs the end-tidal CO 2 tension is 0508 kPa less than the arterial CO 2 tension and is a useful non-invasive estimate of arterial CO 2. PubMed Add filter Published by Danish medical journal 01 September 2019.
A more complete picture of carbon dioxide transfer can be obtained from a capnogram similar to an ECG tracing. Current guidance recommends an end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 of 4045 kPa 300338 mm Hg to achieve a low-normal arterial partial pressure of CO2 PaCO2 and reduce secondary brain injury. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring or capnography End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 monitoring is an attractive method as it is non-invasive portable and relatively inexpensive.
The technique has been End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in neonates Carbon dioxide monitoring is vital in the management of ventilated newborn babies. Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective alveolar CO 2 reflects arterial CO 2. Normally the end tidal appears as a plateau on the capnograph.
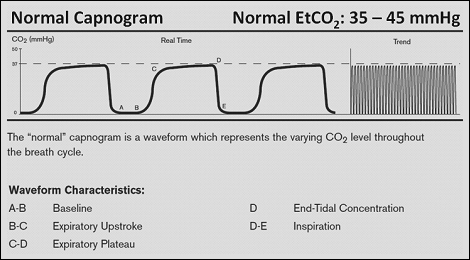
There is a rapid rise in CO2 as expiration continues. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle.
The graphical representation of the concentration or partial pressure of expired carbon dioxide during a respiratory cycle is shown in a waveform format. Deakin et al. Because of the leak in the circuit the carbon dioxide is escaping rather than being measured.
The normal Range of Co2 is 35-45mmHg and this is measured at the end-tidal point of the alveolar plateauas described below. In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Assess vital signs for decompensation 0 2 sat BP HR RR and LOC 3.
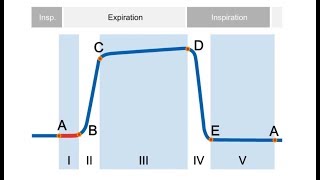
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. Phases of the waveform. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
Subsequently one may also ask what does it mean. You can see that the plateau is not there and the return to the baseline happens rather quickly. EtCO 2 is the maximum expired carbon dioxide concentration during a respiratory cycle.

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar
Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice

End Tidal Oxygen Measurement White Paper Clinical View

Carbon Dioxide Monitoring In Children A Narrative Review Of Physiology Value And Pitfalls In Clinical Practice Humphreys 2021 Pediatric Anesthesia Wiley Online Library

Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice
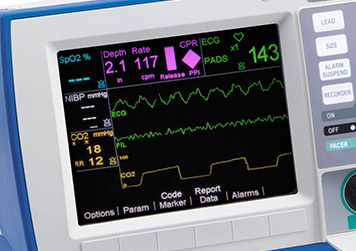
End Tidal Co2 Etco2 Capnography For R Series Zoll Medical

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology
End Tidal Capnography Background Indications Technical Considerations

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration E Co2 Mm Hg For The Download Scientific Diagram

Easy Cap End Tidal Colorimetric Co2 Detector Reflex Medical
E Learning Basics Of Capnography Youtube
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk

E Learning Basics Of Capnography Youtube

The Morphology Of The Normal Capnogram Etco2 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Icu Nursing Paramedic School Human Anatomy And Physiology